Warts are multiple skin growths that appear on the arms, elbows, legs, face and even the genital region. They have a round shape, protrude above the surface of the skin and, if mechanically damaged, bleed and cause discomfort. Externally, such formations seem quite harmless, but in fact their appearance indicates the presence of the human papillomavirus in the body.
The doctors' verdict when these tumors appear is to remove them as quickly as possible. This is the only way to avoid unpleasant consequences and completely eliminate the existing cosmetic defect. There are many methods for removing warts, each of them has certain characteristics and indications. Let's find out what methods are used in modern dermatology and how to recognize the presence of warts on the body.
Important!
The information in this article cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-medication. To make a correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment, you should always consult a doctor.
What is a wart?
This is a benign skin-colored formation that represents a localized proliferation of the epidermis with papules (nodules) or plaques. Simply put, such formations do not differ or differ slightly in color from the skin, but rise above its surface and have a characteristic round shape.
Complications of warts include cracking of the surface, growth of the affected areas, and joining the infection process. Additionally, some types of growths are painful. But most often patients do not think about the possible consequences and seek help from a doctor for only one reason - the unaesthetic appearance of the growths and psychological discomfort due to their appearance.
Warts, as a rule, do not degenerate into malignant neoplasms. However, externally they can be confused with some types of malignant pathologies. Therefore, medical examination when such growths are detected is a mandatory measure to maintain health.
Photo gallery
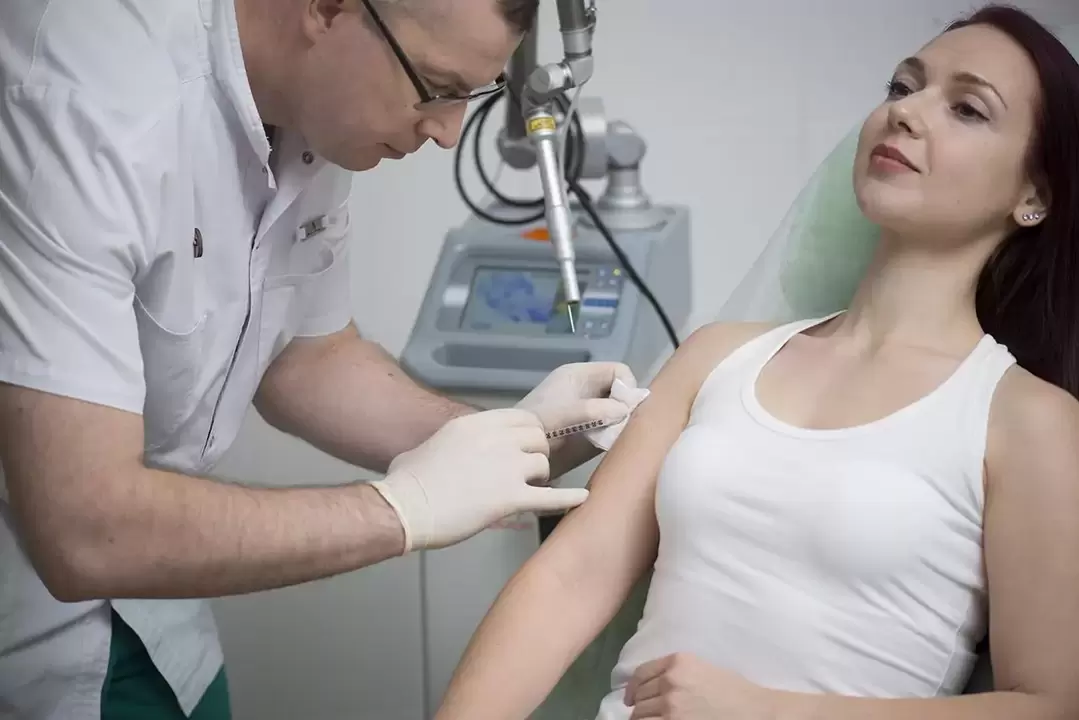
Reasons for the appearance
The cause of warts on the body is the presence of papillomavirus (HPV) in the body. One of the symptoms of this infection is light-bodied neoplasms, which are often multiple in nature.
According to statistics, up to 90% of the world's population is infected with papillomavirus. More than 100 types of HPV have been identified that can infect the skin and mucous membranes and cause the development of changes characterized by papillomatous growths.
Once in the body, papillomavirus infection does not always provoke the development of external manifestations. This is facilitated by just a few factors, including:
- avitaminosis;
- bad habits;
- pregnancy;
- endometriosis, etc.
Furthermore, the development of HPV can also occur against the background of a normally functioning immune system. It is worth noting that infection occurs through direct contact with an infected person. The most common methods of infection are through sexual contact with a person infected with the human papillomavirus or transmission from a parent to a child. Furthermore, the growths on the skin (i. e. , warts) themselves are contagious. It is also known that the virus can penetrate the basal layer of the epidermis through microtraumas.
It is worth mentioning that HPV does not always cause warts, as it can occur in a latent (hidden) form. Also, the appearance of tumors depends on the subtype of infection that has entered the body. The lesions caused by the human papillomavirus are morphologically diverse, therefore only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.
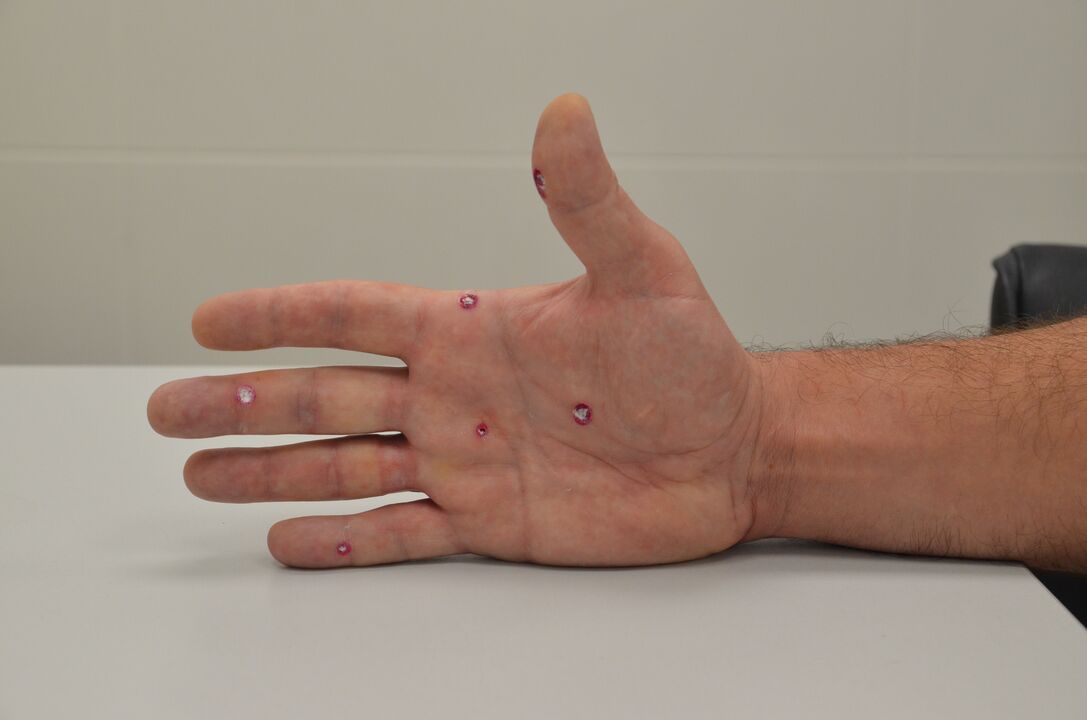
Photo gallery
Types of warts
The human papillomavirus can cause the following formations:
- Common or vulgar (verrucae vulgaris). The most common form, most common in preschool children (approximately 70% of cases). These are protuberances with a rough surface up to several millimeters in size. You can presentyellowish or grayish color. At first, the shade usually matches the skin tone, but then the formations begin to darken. Over time, they can increase in size, causing the person great discomfort. Furthermore, there are frequent cases of cracks appearing around the wart. To the touch - rough and dense, covered with keratinized skin on top. The main location is the fingers, back of the hands, in children growths are also found on the knees. Often around a vulgar wart a cluster of several small warts forms, and over time the affected areas only increase in size. As a rule, the formations are not painful, but in rare cases they can disappear on their own. But most of the time its removal is necessary to avoid injuries. The cause of the appearance of warts of this type are HPV types 1, 2, 4 and 7. Infection occurs through direct contact with a patient. There are also a series of factors that predispose to infection: presence of microtraumas on the skin, recent shaving, hyperhidrosis, excessive pressure on the skin from clothes or shoes. Children often become infected at school, kindergarten or in the sports section. When identifying neoplasms of this type, it is important to make a differentiated diagnosis and exclude the presence of verrucous cutaneous tuberculosis, keratoacanthoma and a series of other pathologies.
- Flat or juvenile (verrucae planoe verrucae juveniles). From the name of these neoplasms it is clear that they appear in adolescence or young adulthood. Its peculiarity is a slight protrusion above the surface of the skin, round shape and color that matches the skin tone. Keratinization is usually absent. The size of the growths is 5–8 mm. They can be single or multiple. Located on the face, neck, back of the hands. They may disappear spontaneously after 1–2 years. Differential diagnosis is made with lichen planus and molluscum contagiosum.
- Plantar (plantar warts). Common form that, as the name suggests, occurs on the soles of the feet. As a rule, this is the area of the metatarsals, heels or tips of the toes - the areas that are subject to the greatest pressure and friction. Such growths can reach large sizes - up to 2 cm in diameter. Excessive friction can cause them to collapse and cause injury. They usually have clear edges and a rough surface. Under the keratinized skin, black dots are often visible - thrombosed capillaries. Color – yellow or brown. The cause of the appearance of such growths are HPV types 1 and 4. The pathological process can be superficial and deep. In the second case, the warts cause discomfort and pain when walking, which is why they are always removed. Differential diagnosis is carried out with calluses and fungal skin lesions.
- Genital warts. This form of neoplasia is one of the common manifestations of HPV in the anogenital region. Condylomas are located on the genitals or near the anus, sometimes found in the groin, armpits, near the mammary glands, and in the corners of the mouth. They are different sizes and look like cauliflower. They are flesh-colored and may have a thin stem or a broad nodule-shaped base. These growths are quite "fragile", so they often bleed. Sexually transmitted. Risk factors include the presence of sexually transmitted infections, frequent changes of sexual partners, disruption of the normal microflora of the vagina, pregnancy, as well as various internal factors (for example, vitamin deficiency). Another characteristic is the simultaneous appearance of multiple genital warts. In men, these formations are often confused with a papular penis collar. In women, the pathology can be confused with micropapillomatosis of the lips.
There are other, less common types of warts. The classification of formations takes into account the type of HPV that caused their appearance, the nature of germination, size and external parameters. For example, A. N. Khlebnikova identifies 8 clinical types of warts. Several researchers identify more options, dividing them into small subgroups. Other common types of neoplasms include the following:
- Filiform warts. Thin horny protuberances that appear on the face: near the nose, mouth, eyes. Generally diagnosed in older patients, they can have a wide or narrow base. Injured very easily.
- Buschke-Levenshtein giant condyloma. This is a separate type of genital wart, which initially appears as a cluster of multiple papillomas. As a rule, the growths are located in the region of the inguinal folds or vulva; over time, an extensive lesion forms with the inclusion of neighboring tissues in the process.
- "Butcher's" warts. This is one of the types of warts vulgaris that appear in people who frequently come into contact with raw fish or meat. They are cauliflower-shaped neoplasms, but the color of skin.
- Cystic warts. A type of growth on the feet that appears as soft knots with deep cracks. When injured, a sticky yellowish-white discharge appears.
Wart diagnosis
In most cases, a visual examination and history are sufficient to make a diagnosis. To confirm the conclusions and exclude other pathologies, a histological examination of the neoplastic cells can be performed.
If another infection is suspected, your doctor may prescribe additional diagnostic procedures. For example, it is possible to perform an analysis to detect antibodies against the virus, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
The treatment of warts, in some cases, depends on the cause of their appearance or, more precisely, on the type of human papillomavirus present. To determine the existing disease, a differentiated analysis of scrapings of epithelial cells from the urogenital tract is carried out.
Removal Methods
The goal of treatment is to remove the growths to prevent regrowth and recurrence. Modern treatment methods provide up to 80% effectiveness. Drug therapy for patients is most often required in the presence of genital manifestations of HPV and includes the use of cytotoxic drugs.
To remove physical manifestations, physical or chemical destruction methods are used. More than 30 different treatment methods are described in modern medical literature, so it is very difficult to talk about a universal method. Yu. Yu. Stirschneider notes that many of the described techniques have a number of serious disadvantages (for example, incomplete radical removal, risk of developing intra- and postoperative complications, formation of various cosmetic defects). That is why the treatment method is chosen individually and only after a differentiated diagnosis.
The most popular treatment methods include the following:
- Cryodestruction. This wart removal method involves exposing the affected areas to liquid nitrogen. Controlled tissue necrosis occurs, resulting in complete removal of the existing tumor. Cryodestruction can be carried out by application (suitable for warts up to 10 mm in diameter) and aerosol (necessary for growths that grow deep into the tissue). Removal takes place in one session, if necessary, the procedure is repeated after 1–2 weeks. This technique is used for a small number of warts (on average up to 4–5 elements) and a small treatment area. The procedure is generally painless and effective, but the result largely depends on the professionalism of the doctor.
- Electrocoagulation. Layer-by-layer removal of the tumor due to the action of electric current. The technique is considered more effective than cryodestruction, but it also has its disadvantages: after removal, scars often remain on the skin. Therefore, this method is not used in cases where a good aesthetic result is important. However, with the help of electric current, large affected areas can be removed.
- Laser destruction. One of the most effective methods for removing warts is laser therapy. This is the preferred method at our Altermed Aesthetic clinic in St. Petersburg. Growth removal occurs layer by layer: under the action of a laser beam, the damaged tissue evaporates until it disappears completely. Exposure time varies from a few seconds to 2–3 minutes (depending on the size and number of growths). The procedure allows you to remove warts, papillomas and condylomas without invasive effects. Due to instant tissue coagulation under the action of a laser beam, the risk of secondary infection is eliminated. Therefore, the rehabilitation process is quick and hassle-free.
- Radio wave therapy. This technique involves the use of electromagnetic waves of a certain frequency. The procedure is carried out using a special device (the Surgitron device is often used). During exposure, tissue heating occurs as a result of evaporation of the forming cells (much like what happens during laser therapy).
- Chemicals. Salicylic patches and lactic-salicylic collodion applications cannot be called a modern method of treatment, however, in some cases, this technique is still used. For example, if there are contraindications to other procedures. Chemical removal is a complex process that requires repeated procedures and preliminary mechanical removal of the affected tissue.
It is very difficult to say unequivocally which method of removing warts is better. When choosing a technique, the doctor takes into account the type of formations, their size, number and location.
The patient's concomitant medical history, the presence of chronic pathologies and previously used methods are taken into account. Studies carried out using popular treatment methods have shown that laser destruction gives optimal results (76%). According to Yu. Yu. Stirschneider, these numbers are higher than those for electrocoagulation (56%) and cryodestruction (44%).
Complications after wart removal are extremely rare. As a rule, consequences are possible after attempts to remove growths on your own. In these cases, the patient presents inflammation, greater spread of the virus through the skin or scar formation. Therefore, if you find a wart or similar formation, do not try to cauterize or cut it yourself.























